Revenue cycle management (RCM) involves overseeing the revenue generated from patients, starting from their initial appointment or interaction with the healthcare system and continuing until their ultimate payment for the cost of care.
It commences with a patient scheduling an appointment and concludes when the healthcare provider has received all necessary payments.
Implementing effective revenue cycle management (RCM) practices is pivotal in minimizing billing errors and optimizing reimbursements from insurance companies.
Within RCM teams, a significant responsibility lies in upholding strict adherence to coding regulations, including vital updates like the transition to the ICD-10 coding system.
This meticulous approach safeguards the financial integrity of healthcare operations and ensures that the entire revenue cycle operates seamlessly, benefiting healthcare providers and their patients.
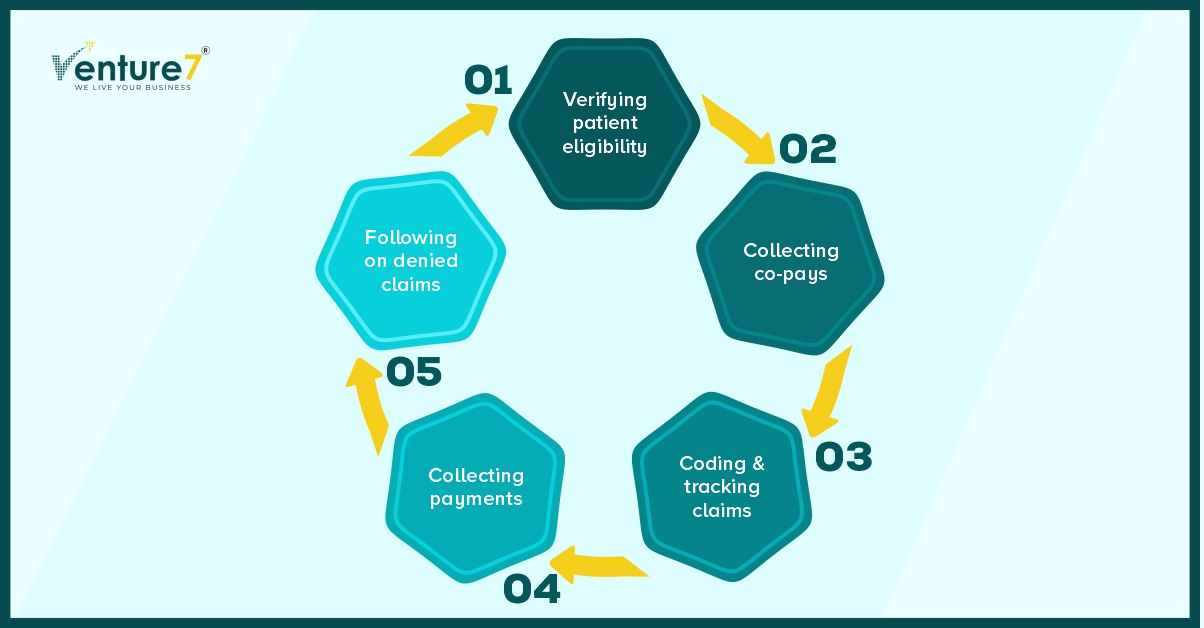
Sequence of RCM Workflow:
Booking Appointments and Checking Eligibility: RCM’s job is to collect and verify patient insurance and demographic details.
Recording Patient Visits and Medical Information: Detailed clinical documentation is essential during the patient’s appointment. Following the directives set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) professionals guarantee the maintenance of precise and all-inclusive records.
This meticulous attention to detail guarantees the quality and accuracy of patient care and billing processes.
Receiving Patient Payments and Co-pays: Significantly impacts the organization’s cash flow.
Superbill Creation: Once the patient has been treated and all necessary information has been collected, the medical reports are translated into diagnosis and procedure codes by a medical coder during checkout.
Subsequently, all the gathered information might be used to compile a report known as a “superbill.”
This report will encompass details such as provider and clinician information, the patient’s demographic data and medical history, particulars about conducted procedures and services, and relevant diagnosis and procedure codes.
Coding and Billing Procedures: For effective coding and billing processes, physicians must utilize a Practice Management system and Electronic Health Record (EHR) that is certified by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
Claim Processing: In the next step, the medical biller takes the superbill and prepares a medical claim sent to the patient’s insurance company.
Submission is the next step once the claim has been checked for accuracy and compliance.
The claim will most likely be electronically transmitted to a clearinghouse, a third-party company that liaises between healthcare providers and health insurers.
There is one exception to the standard procedure, which applies to high-volume payers like Medicaid. These payers are willing to receive claims directly from healthcare providers.
Payment Received: This can either be getting reimbursement from the insurers or following up directly with the patient. In case of claim denials, the RCM should send the requested information.
Key Revenue Cycle Management Challenges and their Impact:
While Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is a critical aspect of maintaining the financial health of healthcare organizations, it comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s delve into some of the common challenges faced in healthcare revenue cycle management:
Billing Errors and Denials:
One of the primary challenges is the occurrence of billing errors leading to claim denials. These errors can range from simple data entry mistakes to more complex coding issues.
Impact: Rejected claims not only delay reimbursements but also require additional resources for correction and resubmission.
Complex Coding and Compliance:
The healthcare industry follows a complex coding system, such as ICD-10, and staying compliant with the frequent updates poses a challenge.
Impact: Non-compliance can result in rejected claims and potential legal issues, emphasizing the need for continuous staff training and system updates.
Patient Eligibility Verification:
Verifying patient eligibility and insurance coverage can be challenging, especially with changing insurance plans and coverage details.
Impact: Inaccurate eligibility checks can lead to claim denials, affecting the revenue cycle and creating dissatisfaction among patients.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs):
The rise of HDHPs means patients are responsible for higher out-of-pocket expenses. Collecting these payments becomes a challenge for healthcare providers.
Impact: Increased financial responsibility on patients can lead to delayed or missed payments, impacting the revenue stream.
Integration of Healthcare Technologies:
Many healthcare providers use different systems for electronic health records (EHR), practice management, and billing. Integrating these technologies seamlessly is a significant challenge.
Impact: Lack of integration can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and delays in the revenue cycle.
Staff Training and Retention:
RCM requires skilled staff who are updated on the latest coding and billing regulations. Staff turnover and training pose ongoing challenges.
Impact: Inadequately trained staff can contribute to errors and inefficiencies in the revenue cycle.
In addressing these challenges, healthcare organizations can benefit from adopting advanced RCM technologies, providing continuous staff training, and fostering a culture of compliance and efficiency. Proactive strategies and regular assessments can help mitigate risks and ensure a streamlined revenue cycle.
Empowering Healthcare Through SaaS Innovation:
In the dynamic realm of healthcare financial management, the advent of Healthcare SaaS Application Development stands out as a transformative force. This revolutionary approach not only signifies a departure from traditional models but also heralds an era of enhanced efficiency and adaptability.
The utilization of cutting-edge technologies is crucial for achieving sustained success in this evolving landscape. Healthcare SaaS applications, with their cloud-based architecture, bring unprecedented flexibility and accessibility. This not only streamlines existing processes but also lays the groundwork for future innovations.
Furthermore, when coupled with the power of adaptive Software Product Engineering, these innovations become a formidable duo. The synergy between SaaS and Product Engineering doesn’t just reduce errors; it creates a robust framework capable of adapting to the ever-changing nature of healthcare revenue cycles. This adaptability is crucial in an industry where norms, regulations, and technologies evolve rapidly.
In conclusion, by embracing these technological solutions and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, healthcare organizations can navigate the challenges of RCM successfully.





